

#Network file synchronization software manual#
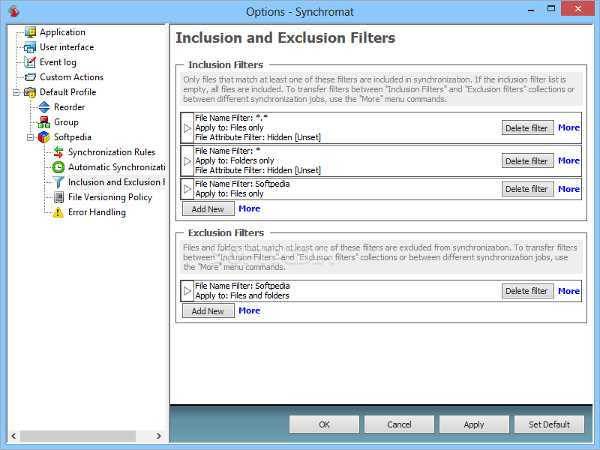
We define synchronization broadly to include both automatic and manual processes and the associated issues of managing files that are shared across devices and among people.
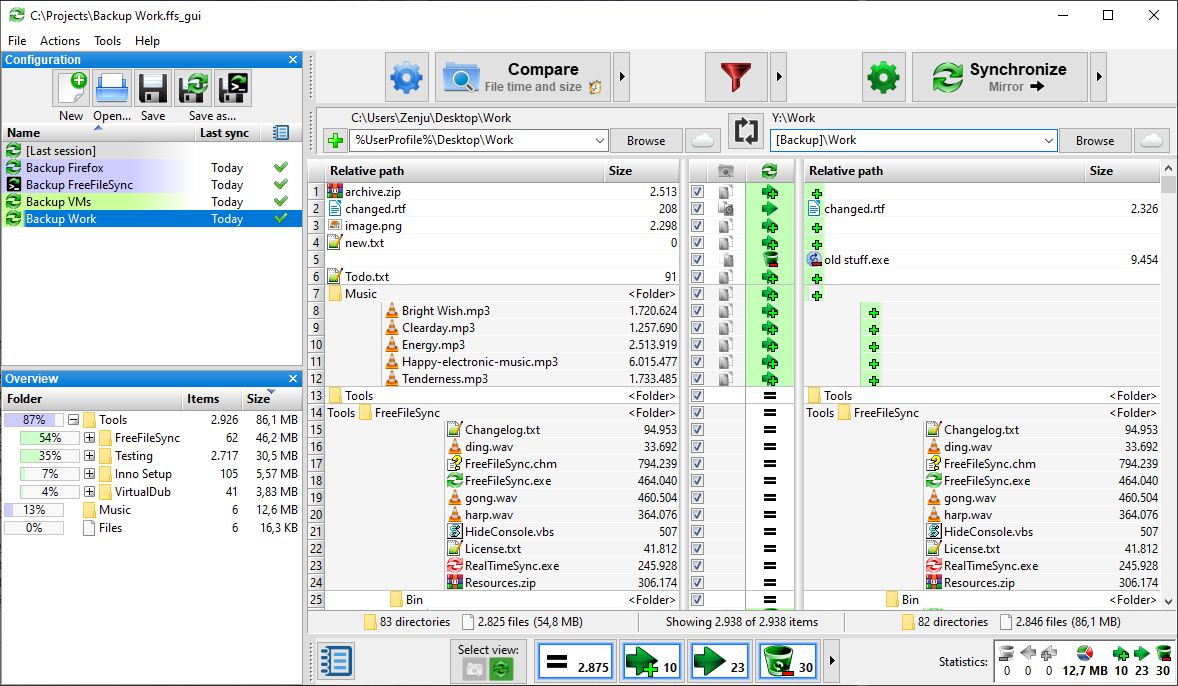
Our research focuses on how people handle the file synchronization and sharing aspects of “personal” information management (including both work and personal information under the person's control). Increasing use of cloud services is spurring practical interest in this topic to inform system designs (Tang, Brubaker, & Marshall, 2013), and more research is needed to help understand users’ needs, practices, and challenges. Yet the cost of synchronization and sharing failures can be significant – users may not be able to access information when or where they need it and may spend considerable time and effort developing practices to work around limitations (Dearman & Pierce, 2008). Relatively little research has focused on how users synchronize data across devices, share data among collaborators, and what problems they encounter when doing so. Many individuals and organizations are making increased use of tools such as Dropbox, Google Drive, and SharePoint to support collaboration and shared access, but these systems can increase data fragmentation and raise concerns about privacy, trust, and control. Users need to have confidence that data will be available when and where they need it, and that they will be able to limit access when desired. This suggests additional challenges and opportunities for synchronization and sharing technologies. Cloud-based services provide new ways to store and share information across people and devices but also add complexity to information management.Ī recent survey of 895 technology experts conducted by the Pew Internet project (Anderson & Rainie, 2010) found that many experts believe the next decade will bring increased adoption of a hybrid computing model in which some work is done in the cloud and some is done on personal devices. Information workers often have multiple computers and mobile devices both at work and at home. Information users today face many challenges in managing information across multiple electronic devices, storage systems, and collaboration tools. Our findings extend research on personal and group information management practices and provide insight for the design of synchronization and sharing systems. We present insights about how boundaries and data separation affect synchronization practices, and about specific synchronization issues users faced when collaborating. We identified several factors that influence users’ choice of methods for synchronization, including privacy and security concerns, data size, institutional policies, and knowledge of systems. Our findings show that while behaviors have evolved as technology changes, users continue to make extensive use of familiar patterns of access, including automated and manual methods. We identify key problems and considerations that influence file synchronization and sharing practices, and describe commonly used strategies. In this paper, we present results of qualitative analysis of interviews with 16 university faculty regarding their use of file synchronization and sharing technologies in their work and personal lives.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
